作者简介: 黄保坤, 1979年生, 江苏海洋大学理学院高级工程师 e-mail: huang_baokun@163.com
燃油发动机的尾气成分检测对于发动机的状态判断、 环境污染监测等具有重要参考价值。 选择以95号汽油为燃料的除草机的发动机作为实验样机, 将发动机排出的尾气直接吹向拉曼积分球光谱仪信号采集焦点, 利用拉曼积分球光谱仪较高的气体检测限和定性、 定量检测所有分子类气体的特点, 对尾气中的气体分子成分进行检测。 探测到尾气的气体成分主要包括N2、 O2、 CO2、 CO、 未燃烧的汽油等。 以氮气振动(2 331 cm-1)的拉曼特征峰强度作为标准, 对O2(1 553 cm-1)、 CO2(1 285和1 388 cm-1)、 CO(2 144 cm-1)、 未燃烧的汽油(2 894 cm-1)的拉曼光谱强度进行归一化处理, 获得其相对拉曼特征峰强度。 对比发现, 空气和汽油挥发混合气的光谱中均未出现CO的特征峰, 汽油挥发混合气中的O2、 CO2含量与空气相比也没有明显变化, 而CO2费米共振峰1 388和1 285 cm-1拉曼特征峰的相对强度比发生变化。 除草机工作状态分为怠速、 一档和二档, 处于工作状态时, 尾气成分中的O2含量均比空气中含量低, 可以定量分析发动机工作过程中消耗的O2量。 而燃油发动机从怠速加速到一档和二档的过程中, 尾气中O2含量相对增加。 这是由于发动机档位的提升伴随着空气的进气量增大, 则参与发动机燃烧的氧气比例相对减少。 与此同时, 尾气中CO2含量相比于空气中的含量急剧增加, 说明燃油发动机工作过程会产生大量的CO2, 且随着档位的提升, 发动机的动力增加, 尾气中CO2比例也逐渐增高。 CO2作为导致温室效应的主要原因, 化石燃料的使用也是其主要来源之一。 数据显示尾气中CO的含量与尾气中汽油的含量成正相关, 说明燃烧不充分的时候, 汽油剩余较多, CO作为不充分燃烧的产物, 其含量也会增加。 随着发动机档位的增加, N2特征峰的绝对强度降低, 这是因为发动机尾气温度升高, 造成氮气的斯托克斯散射强度降低。 利用拉曼积分球光谱仪对不同状态下发动机尾气成分的变化进行分析, 并初步建立发动机状态与气体浓度变化的关系。 对拉曼积分球技术应用于燃油发动机尾气检测进行了初步探索并验证了其可行性。
The detection of the exhaust gas components of a fuel engine has important reference values for engine condition determination and environmental pollution monitoring. For this study, a weedkiller engine powered by No.95 gasoline was chosen as the experimental prototype, and the exhaust gas from the engine was blown directly into the signal acquisition focus of the Raman integrating sphere spectrometer. The high gas detection limit and the ability of the Raman integrating sphere spectrometer to probe all molecular gas qualitatively and quantitatively have been used to probe the molecular component of the gas in the tails. The gas component detected in the trailing gas is dominated by N2, O2, CO2, CO, and unburned gas. The relative Raman characteristic peak intensities of O2 (1 553 cm-1), CO2 (1 285 cm-1 and 1 388 cm-1), CO (2 144 cm-1), and unburned gasoline (2 894 cm-1) were obtained by normalizing the Raman spectral intensities using the Raman characteristic peak intensity of nitrogen vibrations as a standard. It can be found that the characteristic peak of CO does not appear in the spectrum of volatile matter of air and gasoline, and the content of O2 and CO2 in volatile matter of gasoline does not change significantly compared with that of air, while the relative intensity ratio of Raman characteristic peak of CO2 Fermi formant 1 388 and 1 285 cm-1 change. The working state of a lawnmower is divided into idler, first and second gear. When operating, the O2 content in the exhaust components is all below that in the air, allowing quantitative analysis of the amount of O2 consumed during engine operation. The O2 content in the exhaust increases relatively when the fuel engine is increased from idle to first and second gear. It is because as the engine gear increases, so does the air intake, and the proportion of oxygen involved in engine combustion is relatively reduced. At the same time, the amount of CO2 in the tailpipe gas increases dramatically compared to the amount in the air, suggesting that the working process of the fuel engine produces large amounts of CO2. The proportion of CO2 in the tailpipe gas gradually increases as the gear is raised and the engine power is increased. One of the main sources of CO2, the main cause of the greenhouse effect, is the use of fossil fuels. The data shows a positive correlation between the amount of CO in the tail gas and the amount of gasoline in the tail gas, suggesting that when combustion is insufficient, there is more gasoline left, and the amount of CO as a product of insufficient combustion also increases. With increasing engine gear, the absolute intensity of the characteristic peak of N2 decreases due to the decrease of the Stokes scattering strength of nitrogen with increasing engine exhaust temperature. In this paper, the Raman integrating sphere spectrometer is used to analyze the changes engine exhaust composition under different conditions. Moreover, the relationship between engine state and gas concentration is preliminarily established. We explore the application of Raman integrating sphere technology to fuel engine exhaust detection and verify its feasibility.
燃油发动机诞生一百多年来, 随着技术不断迭代更新, 已应用于生产和生活的各个领域。 发动机尾气的排放, 成为了大气污染主要来源, 准确定性、 定量检测尾气中各组分含量对尾气的治理具有重要意义, 也可为发动机燃油供给系统和点火系统工作状况的评估提供参考[1]。 温度和压力对尾气的检测结果具有很大的影响, 例如燃油发动机的燃料在温度较高时为气态, 温度降低时为液态, 因此必须保证原位、 实时的检测条件, 才能保证检测结果的准确性。 传统的气体传感器, 检测范围较窄, 稳定性差, 且可能与其他杂质气体产生反应, 造成测量结果偏差[2]。 红外吸收光谱技术, 具有高分辨率、 高灵敏度等特点, 被广泛应用于气体检测中, 但多组分共存时, 普遍存在谱峰重叠现象[3]。 相较而言拉曼光谱检测技术具有独特优势, 现已应用于电化学[4]、 纳米化学[5]、 催化反应[6]以及物理化学[7]等领域。 其中拉曼积分球光谱仪可以原位、 实时、 无损地对多成分混合气体中所有的分子类气体(不包括惰性气体)进行检测, 并且具有较高的空间分辨率, 适用于气体分子分布梯度的检测[8]。
采用自主研制的拉曼积分球光谱仪[9], 激发光源为Cobolt公司的532 nm固体激光器, 输出功率500 mW, CCD为Andor公司的316LDC-DD, 光谱仪的光谱范围为800~3 100 cm-1, 分辨率约3 cm-1。 首先测量空气的拉曼光谱和95号汽油挥发后的空气拉曼光谱, 曝光时间均为180 s, 测得拉曼光谱图如图1(a—d)所示, 空气的拉曼光谱中包括拉曼频移在1 553和2 331 cm-1的O2和N2的振动峰, 以及在1 285和1 388 cm-1的CO2的费米共振峰, 含有汽油挥发物空气的拉曼光谱除了包含空气中O2和N2的拉曼特征峰外, 还包括汽油的拉曼特征峰, 其位置分别为: 996、 1 008、 1 035、 1 057、 1 073和1 212 cm-1。 在2 800~3 200 cm-1范围是汽油多种成分C—H键混合在一起的拉曼特征峰, 其主峰位置为2 894和2 956 cm-1。
 | 图1 空气和含有汽油挥发物的空气的拉曼光谱图(a, b, c, d)Fig.1 Raman spectra of air and air containing gasoline volatiles (a, b, c, d) |
图2为发动机尾气原位检测的展示图, 在实验过程中, 将除草机尾气排放口对准拉曼积分球的样品检测焦点, 实时检测除草机尾气排放的组分和含量。
在除草机发动机的工作过程中, 氮气基本上不参与燃烧。 而数据显示, 随着发动机转速的增加, 氮气的绝对峰强呈现下降趋势。 这是因为燃烧室在燃烧过程中, 温度升高, 导致斯托克斯散射强度下降, 而且尾气中各气体组分的拉曼绝对峰强均有所下降。 为了消除发动机燃烧过程中温度带来的影响, 以氮气作为尾气气体成分定量分析的内标物质, 对特征峰光谱强度做归一化处理, 如图3(a—d)所示, 对各组分特征峰强度归一化处理后数据如表1所示。
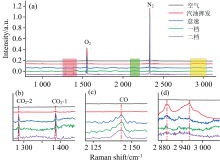 | 图3 空气、 含汽油挥发物的空气和燃油发动机不同档位时的尾气的归一化拉曼光谱图(a, b, c, d)Fig.3 Normalized Raman spectra of air, air containing gasoline volatiles and exhaust gas of a fuel engine in different gear locations(a, b, c, d) |
| 表1 各组分相对峰强 Table 1 Relative peak intensity of each component |
发动机档位提升后, 会有更多的汽油挥发物和空气进入发动机燃烧室燃烧, 进而提高发动机的输出功率。 观察数据可发现, 在归一化后的尾气组分含量的数据中, 氧气相对含量升高, 这是由于档位加大, 燃烧室内的进气量变大, 未参与燃烧的氧气过剩所导致的。 二氧化碳是汽油中含碳化合物充分燃烧的表征, 档位变换后, 二氧化碳浓度的升高则是空燃比提升的体现, 也是发动机动力提升的依据。 与此同时, 尾气中一氧化碳与汽油的相对峰强则是随着发动机怠速, 一档, 二档的变化, 先上升后下降。 一档与怠速相比, 汽油需求量与进气量同时增加, 因未燃烧充分, 从而导致尾气中剩余汽油增加, CO含量增加。 与一档相比, 二档尾气中的CO与汽油含量都下降, 说明发动机在此状态下, 汽油燃烧更加充分。 二档与怠速状态下的CO含量相对不变, 而在二档汽油量增加的同时, 汽油的剩余量却更小, 相比较而言, 二档状态下发动机的空燃比最大, 输出功率更大。
通过自主研制的拉曼积分球光谱仪, 利用其高空间分辨率的优点, 实现了除草机燃油发动机尾气的原位测量, 并对尾气中N2、 O2、 CO2、 CO、 未燃烧的汽油的含量与发动机档位的关系进行了分析, 验证了拉曼积分球光谱仪在燃油发动机尾气检测方面的可行性, 对于环境保护、 发动机状态检测等提供了一种原位检测的工具。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|



