作者简介: 史冬冬, 1996年生, 陆军工程大学基础部硕士研究生 e-mail: shidongdongjiayou@163.com
稀土锆酸盐(RE2Zr2O7, RE为稀土元素)体系材料具有热导率低、 高温相结构稳定、 抗化学腐蚀和价格相对低廉等优势, 近年来在热障涂层、 环境障涂层和核防护涂层等领域得到广泛而深入的应用, 获得了广泛关注。 然而, 目前对该涂层材料的研究主要还是集中在热学、 力学及电学性能等, 对光学性能特别是反射光的偏振特性研究则鲜见报道。 以锆酸镧(La2Zr2O7)为代表, 系统研究了稀土锆酸盐光学偏振特性, 特别分析了材料表面属性与光学偏振特性的对应关系。 实验中利用固相反应法分别合成制备了La2Zr2O7粉体和致密块体材料, 并利用XRD(X-ray diffraction), Raman spectra和SEM (scanning electron microscope)等分析表征其微观结构, 结果显示制备的La2Zr2O7材料为立方焦绿石相结构。 在光学性能分析中, 分别用自然光和线偏振光作为探测光源, 在不同探测角下研究其反射光偏振特性。 研究表明, 对于自然光入射, La2Zr2O7块体和粉体材料的线偏振度(DOLP)与入射光波长呈现显著的依赖关系, 随着波长的增加, DOLP呈现出先增大后减小的趋势。 值得注意的是在红外波段, DOLP迅速降低并接近于0, 表明该材料在红外波段表现出良好的偏振隐身特性。 研究还发现, 在自然光入射时, 致密块体材料的DOLP分别在波长~720和~773 nm出现极大值, 且峰值波长对探测角度不敏感, 粉体材料在~714和~774 nm附近也出现两个峰。 在线偏振光入射, 块体材料在大角度探测角下, DOLP在~720和~763 nm出现两个峰, 与自然光入射光不同的是, 同一个探测角下两个峰的峰值大小基本相同, 粉体材料则在~720和~755 nm附近出现两个峰, 且峰值强度减弱, 说明涂层材料的粗糙度对反射光的偏振特性有一定影响, 研究进一步显示, 两个峰值对应的波长与探测角无显著依赖关系。 本研究结果为稀土锆酸盐涂层材料的偏振光谱学的开发、 应用和设计提供理论和实验支撑。
Rare earth zirconate (RE2Zr2O7, RE is rare earth element) materials have the advantages of low thermal conductivity, stable high-temperature phase structure, corrosion resistance and relatively low price, etc. In recent years, it has been widely and deeply applied in the fields of the thermal barrier coating, environmental barrier coating and nuclear protective coating and has attracted extensive attention.However, the current research on these coating materials is mainly focused on thermal, mechanical and electrical properties, while the optical properties, especially the polarization characteristics of reflected light, are rarely reported. Therefore, taking La2Zr2O7 as the representative, the optical polarization characteristics of rare earth zirconate were systematically studied, especially the corresponding relationship between material surface properties and optical polarization characteristics was analyzed. In the experiment, the powder and density bulk of La2Zr2O7 were synthesized by the solid-state reaction method. The microstructure was analyzed and characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), Raman spectroscopy and scanning electron microscope (SEM). The results show that the prepared La2Zr2O7 is a cubic pyrochlore phase structure.In the analysis of optical properties, natural light and linearly polarized light were used as detection light sources, respectively, and the polarization characteristics of reflected light are studied under different detection angles.It is shown that, for the natural light incidents, the degree of linear polarization (DOLP) of both bulk and powder La2Zr2O7 materials is significantly dependent on the incident light wavelength. With the increase of wavelength, the DOLP increases first and then decreases. It is worth noting that the DOLP decreases rapidly and approaches zero in the infrared band, indicating that the material shows good polarization stealth characteristics in the infrared band. It is also found that the DOLP of dense bulk has amaximum value at ~720 and ~773 nm while natural light is incident, and the peak wavelength is not sensitive to the detection angle. Powder materials also have two peaks near ~714 and ~774 nm. Under the incidence of linearly polarized light, for the large angle detection angle, DOLP of bulk has two peaks at ~720 and ~763 nm respectively. Different from the incidence of natural light, two peak values are equal under the same detection angle. Two peaks near ~720 and ~755 nm respectively appear for powder materials, and the peak intensity decreases, indicating that the roughness of the coating material has a definite influence on the polarization characteristics of the reflected light.Further research shows that the wavelength corresponding to the two peaks does not become dependent on the detection angle. The results of this study provide theoretical and experimental support for the development, application and design of polarization spectroscopy of rare-earth zirconate coating materials.
在复杂环境中, 考虑到单一材料不能满足越来越高的性能需求, 近年来, 涂层材料与基底材料的结合得到广泛而深入的应用。 其中, 涂层材料的光学性能特别是反射光的偏振光谱特性越来越引起人们的关注[1]。 反射光的偏振特性受照明条件、 环境湿度、 能见度、 观测位置的影响较大[2], 对材料表面反射及散射光偏振特性分析, 可以用于空间目标的有效探测[3], 如对卫星表面进行偏振探测, 可以获得其表面损坏程度[4]。 对于伪装涂层材料, 利用偏振探测可以获得偏振程度与波长、 探测角和方位角的对应关系等[5], 对于金属目标, 利用偏振特征可以反演目标纹理、 表面结构以及材料类型等[6]。 近年来, 作为一种新型涂层材料, 稀土锆酸盐(RE2Zr2O7, RE为稀土元素)材料体系由于具有低热导率, 高温相结构稳定、 抗腐蚀和价格相对低廉等优势, 在多个领域得到广泛的应用[7], 目前其热学、 力学性能获得较多研究[8, 9, 10], 但对于其光学性能特别是反射光偏振特性的研究则鲜见报道。 本工作选取具有代表性的La2Zr2O7为研究对象, 通过固相反应法实验制备其块体和粉体材料, 分别利用自然光和线偏振光作为入射源, 系统研究该材料反射光谱偏振特性。
实验中采用固相反应法制备La2Zr2O7样品, 将La2O3和ZrO2氧化物粉末在800~1 000 ℃下煅烧1 h, 再用无水乙醇作为液体介质, 以氧化锆为球磨, 根据化学计量比称量氧化物粉末混合球磨, 球磨机转速为250~300 r· min-1, 球磨时间24 h; 采用旋转蒸发仪对浆料进行蒸发, 置于干燥箱在120℃蒸干干燥12 h, 在研磨后分别过200目和400目筛, 将粉体压制初始素坯后将成型坯体经220 MPa冷等静压2 min, 为释放静压过程中产生的内应力, 将样品置于干燥箱中放置24 h。 烧结过程采用无压烧结, 温度控制参数为: 室温至1 000 ℃, 升温速率为5 ℃· min-1, 高温段1 000~1 600 ℃为升温速率为3 ℃· min-1, 并在1 600 ℃保温10 h, 保温后降温速率为5 ℃· min-1。 块体样品进行抛光处理, 成相粉体的制备与上述工艺参数相同。
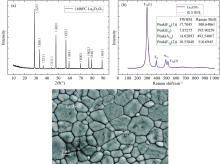
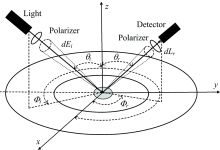
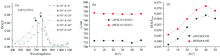
制备得到的样品晶体结构信息X射线衍射及Raman光谱及微观形貌分别如图1(a— c)所示, 结合XRD, Raman和SEM微观形貌分析表征可以看出所制备的样品为纯净立方焦绿石相, 块体样品晶粒发育完整, 无第二相产生。 光学偏振特性测试, 采用的实验平台结构如图2所示, 在x-y平面中心处放置样品, 样品的直径为15 mm, 厚度为0.7 mm, 光源的投影与y轴夹角为Φ i, 探测器的投影与y轴的夹角为Φ r, θ i, θ r则分别为光源和探测器与z轴的夹角。 光源处利用偏振片作为偏振光产生器, 探测器处的偏振片控制探测器接收的辐射亮度。
采用斯托克斯(Stokes)矢量来描述光与物质表面相互作用后反射光的偏振特性[11]
式(1)中, I为总光强, Q为是0° 与90° 线偏振的强度之差, U为45° 与135° 线偏振的强度之差, V为光场中右旋圆偏振分量与左旋圆偏振分量光强之差。 由于Stokes矢量中的V很小, 几乎可以忽略不计[12, 13], Stokes矢量通过式(2)获得
考虑到目标与背景偏振度对比效果, 最好的间隔范围为40° ~80° , 因此采用改进的Pickering方法[14], I, Q和U分别通过旋转偏振片0° , 45° , 90° 和135° 测量探测器接收的辐射亮度求解。 目标的偏振信息中, 线偏振度(degree of linear polarization, DOLP)是重要指标, 该参量与物体表面的状态和属性相关, 线偏振度DOLP定义见式(3)
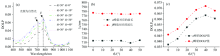
首先用自然光作为入射光源, 入射角θ i为30° 固定不变, 探测角范围为0° ~50° , 步长为10° , 由图3(a)可知, La2Zr2O7块体的DOLP光谱曲线总体来看在可见光区域变化显著, 在约500 nm开始大幅上升, DOLP分别在波长~720和~773 nm出现两个极大值, 分别用α 和β 来标记。 将α 和β 峰值对应的波长λ 0和峰值强度DOLPmax两个特征参数从图3(a)中提取出来, 分析结果见图3(b), 可以看出随着探测角θ r逐渐增大, α 和β 峰峰值对应的波长λ 0的变化不明显, α 和β 峰的峰强度DOLPmax对探测角度有明显依赖关系[如图3(c)所示], 呈现出先增大后急剧减小的规律。
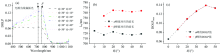
为了研究涂层材料的粗糙度对偏振信息产生的影响, 采用La2Zr2O7粉体做相应的测试, 结果如图4所示, 结合图3(a)和图4(a)中对比分析, La2Zr2O7粉体和块体材料的DOLP光谱曲线总体趋势大致相同, 在~714和~774 nm附近也出现两个峰。 根据图4(b)和图4(c), 随着探测角θ r的增大, α 和β 峰的峰值对应的波长λ 0变化有限, 但是对比图3(c)和图4(c)可以看出, 粉体材料的DOLPmax随探测角度增加达到峰值后减弱的趋势显著变缓。
无论是对于遥感技术还是伪装物体识别, 偏振探测可以更加精确地识别目标。 以偏振光作为入射光源, 进一步研究La2Zr2O7材料表面反射光的偏振特性。 如图5(a)所示, 对于La2Zr2O7块体材料, 在可见光波段偏振光入射时, 探测角θ r为0° 和10° 时DOLP对波长的变化不敏感, 但是当探测角θ r≥ 20° 时, DOLP随波长增加变化较为显著, 且在~720和~763 nm出现两个峰。 相比于自然光入射, 在线偏振光下入射时反射光谱出现了峰强度明显增大, 因此反射光偏振度增加, 所以探测光源的选择会对La2Zr2O7表面反射的偏振信息产生显著影响。 此外, 从图5(a)可以看出在偏振光入射下, 在近红外波段DOLP近似为0, 说明La2Zr2O7涂层材料在近红外波段范围内反射光的偏振程度可以忽略不计, 有利于此类材料的红外偏振隐身设计。 α 和β 峰的大小与探测角度关系见图5(b), 随着探测角的增大, α 和β 峰峰值对应的波长λ 0分别在~720和~763 nm附近; 如图5(c)所示, α 和β 对应的DOLPmax波峰曲线基本保持了同步, 说明La2Zr2O7块体对入射光电场矢量在x-y平面内的取向变化不敏感。
对于La2Zr2O7粉体材料, 从图6(a)可以看出, DOLP总体的趋势大致与La2Zr2O7块体一致, 在~720和~755 nm出现两个峰, 但是在小角度入射下, α 和β 峰差异很小, 相比于块体, 峰值差异相对减弱, 说明在偏振光照射下, La2Zr2O7材料的粗糙度对其反射偏振光的光学性质有确定影响。 从图6(b)和图6(c)可以看出, 其α 峰峰值对应的波长λ 0仍稳定在~720 nm, β 峰稳定在~755 nm。 相对于块体材料, 粉体材料的DOLPmax曲线在探测角大于40° 时变化缓慢。 需要指出的是光源入射角为θ i为30° , 理论上探测角θ r为30° 时DOLP出现镜向峰值, 本实验中无镜向峰值出现可能是因为La2Zr2O7表面粗糙度大于或等于相应波段光波的波长[15]。
利用固相反应法制备了高质量的La2Zr2O7块体和粉体样品, 分别在自然光和线偏振光入射下, 系统地研究了其反射光谱偏振特性。 研究发现, La2Zr2O7块体和粉体材料在不同光照条件下DOLP对入射光波长有显著依赖关系, 在自然光照射下, DOLP随着波长的增加呈现出显著先上升后降低的特性, 特别是在接近红外波段DOLP到达峰值后大幅降低, 且随着波长的增加接近于零, 表现出优异的红外偏振隐身特性。 在线偏振光入射时, DOLP随着波长的增加呈现两个峰值, 且块体材料比粉体材料更加显著, 说明粗糙度对反射光的偏振特性有确定影响。 研究还发现, 随着入射探测角度的增加, La2Zr2O7块体材料和粉体材料的DOLPmax都呈现出先上升后降低的特性, 然而入射探测角度对DOLPmax对应的峰值波长影响有限。 本工作的主要结论对高性能稀土锆酸盐涂层材料的反射光谱设计和拓展应用具有一定的科学价值。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
|
| [15] |
|