作者简介: 徐昕霞, 女, 1993年生, 钢铁研究总院硕士研究生 e-mail: 1205606176@qq.com
常见的玩具材料有聚氯乙烯(PVC)、 聚丙烯(PP)、 聚苯乙烯(PS)等。 为了使玩具塑料有更好的延展性, 有利于塑料成型, 在加工过程中会加入一定量的塑化剂。 邻苯二甲酸酯类(PAEs)塑化剂种类繁多, 用途最为广泛, 是玩具塑料中最普遍使用的塑化剂。 常见的PAEs有邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己基)酯(DEHP)、 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBP)和邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯(BBP)。 研究表明, PAEs的分子结构与雌性激素类似, 被称作“环境荷尔蒙”。 长期或高浓度接触可造成内分泌紊乱, 影响男性生殖能力、 促使女性早熟、 危害儿童生殖系统。 北京海关指出, 由于PAEs增塑剂含量超标导致玩具不合格的占比最大。 在玩具进出口环节, 必须进行抽检PAEs增塑剂的含量以保证安全通关。 现行玩具塑料中PAEs的检测方法, 存在前期处理过程复杂、 检测设备昂贵、 对操作人员的专业要求较高等缺点, 不利于PAEs的快速检测, 迫切需要开发一种快速准确检测玩具塑料中PAEs含量的方法。 以DEHP, DBP和BBP为研究对象, 建立激光拉曼光谱快速筛查PAEs塑化剂的方法。 首先, 采用密度泛函理论(DFT)计算了三类塑化剂分子振动光谱, 并与其在拉曼光谱仪上测得分子拉曼光谱比对认定, 表明该方法对PAEs分子拉曼光谱特征峰的归属正确, 能够用于玩具塑料样品的定性分析。 其次, 研究了拉曼光谱仪快速直接定量检测塑料中PAEs含量的方法。 结果表明DEHP, DBP和BBP的含量与其特征峰强度呈线性相关, 相关系数分别为0.98, 0.99和0.99, 表明PAEs定量分析的准确度较高。 最后, 采用该方法在不经任何前处理的条件下, 测试市售玩具样品。 通过优化采集过程中的背景扣除方法, 获得拉曼光谱, 确认了PAEs的种类为DEHP, 并计算出DEHP的含量。 同时, 采用气相色谱-质谱法(GC-MS)准确检测样品中PAEs的种类及含量, 两种方法的一致性令人满意。 因此, 采用激光拉曼技术, 通过优化处理过程, 可快速、 无损检测塑料玩具中PAEs的种类及含量, 能够大大缩短检测时间, 节约测试成本。 并有望应用于海关现场, 提高通关速度。
Many plastics can be used to make toys, such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polypropylene (PP), polystyrene (PS), etc. A certain amount of plasticizer will be added to the plastics in production, in order to make the toys have better ductility and formability. It is generally known that the phthalate esters (PAEs) are widely used plasticizers in toy plastics. The common PAEs are diethylhexylphthalate (DEHP), dibutyl phthalate (DBP) and butyl benzyl phthalate (BBP). Research suggests that the molecular structure of the PAEs is similar to estrogen, so the PAEs is also called “environmental hormone”. The PAEs can cause endocrine disorders, affect male reproductive ability, promote premature female puberty, and endanger children’s reproductive system in long-term or high concentration environments. Beijing Customs pointed out that the proportion of excessive PAEs was the largest in the unqualified toys. Therefore, sampling inspection is needed to ensure safety in the import and export of toys. The current standard test method of PAEs in toy plastics in China’s Customs has some shortcomings, such as complex pre-treatment process, expensive testing equipment and high professional requirements for operators, which is not conducive to the rapid detection of the PAEs and seriously restricts the rapid customs clearance of toys. Therefore, it is urgent to develop a rapid and accurate method to detect the PAEs content in toy plastics. The purpose of this paper is to establish a rapid screening technology for the PAEs in toy plastics. Firstly, the molecular configurations of DEHP, DBP and BBP were optimized, and the molecular vibration spectra were calculated by density functional theory (DFT). On this basis, the Raman spectra of DEHP, DBP and BBP measured by laser Raman technology were identified and the molecular vibration modes were assigned. This result is reliable and consistent with the actual spectral data. It shows that this method can correctly assign the characteristic peaks of Raman spectra of PAEs molecule and can be used for qualitative analysis of DEHP, DBP and BBP. Secondly, we studied the method of rapid and direct quantitative determination of the PAEs in plastics by Raman spectrometer. The results showed that the content of the DEHP, DBP and BBP were linearly correlated with the intensity of its characteristic peak, and the correlation coefficient was 0.98, 0.99 and 0.99, respectively, which indicated that the method had a high accuracy in quantitative analysis of the PAEs. Finally, the laser Raman spectrometer was used for the first time to test toy samples on the market without any pretreatment. The Raman spectra of children’s toys were obtained by optimizing the background subtraction method in the collection process. The type of the PAEs was identified as the DEHP by characteristic peaks, and the content of the DEHP was calculated. Meanwhile, the type and content of the PAEs in toy plastics were further detected by GC-MS. The consistency of the two methods was satisfactory. In conclusion, the rapid detection of the types and contents of the PAEs in plastic toys by laser Raman technology can shorten the detection time of plasticizers in children’s toys without damaging toys, and save testing costs. This method can also be applied to the qualitative and quantitative analysis of the PAEs plasticizer in other solid samples, and it is expected to be applied to the customs site to improve customs clearance speed.
中国是儿童玩具生产和出口大国, 世界上约75%的玩具在我国生产。 玩具塑料一般要求具有良好的延展性和可成形性。 更重要的是, 由于直接接触人体, 特别是儿童, 玩具塑料对于安全性的要求特别高。 而邻苯二甲酸酯(phthalate esters, PAEs)的出现极大程度提高了玩具塑料的延展性。 PAEs塑化剂种类较多, 其中以邻苯二甲酸二(2-乙基己基)酯(DEHP)最为常见, 占塑化剂产量的75%, 其次为邻苯二甲酸二丁酯(DBP)和邻苯二甲酸丁苄酯(BBP)。 然而, PAEs的分子结构与雌性激素类似, 被称作“环境荷尔蒙”。 长期或高浓度接触可造成内分泌紊乱, 影响男性生殖能力促使女性早熟。 除此之外, PAEs还具有生殖毒性、 胚胎毒性、 肝脏毒性、 心脏及神经毒性、 致突变作用和致癌作用等[1]。 如孕期母体过多暴露于PAEs环境下, 可能导致胎儿畸形或DNA结构破坏[2]。 特别是对于处于生殖系统发育时期的儿童, 此类物质的危害更为严重, 因而世界各国对儿童玩具中PAEs的添加量有严格的规定。
鉴于PAEs对人体有诸多健康影响, PAEs的定性定量检测就显得十分重要。 目前, PAEs的检测方法主要有: 气相色谱-质谱法(GC-MS)[3]、 高效液相色谱法[4]、 傅里叶变换红外光谱法[5]、 超声萃取法[6]、 微乳毛细管电动色谱法[7]、 荧光分光光度法[8]、 离子追踪-气相色谱法[9]等。 上述方法虽然可以准确定性定量PAEs, 但是存在很多问题, 如前处理复杂, 耗时长, 有机溶剂使用量大, 仪器及检测费用昂贵, 对操作人员有一定的专业要求等, 因而无法满足PAEs现场快速检测的迫切要求。
近年来, 激光拉曼光谱技术以其突出的优势成为PAEs快速筛查的常用手段, 大多数研究集中在食品领域, 包括酒、 饮料、 牛奶中的塑化剂快速检测, 通常需要结合表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)技术。 例如, Liu等通过液-液自组装制备了单层纳米金薄膜, 结合拉曼光谱仪测定了市售白酒中的BBP[10]。 Jiang等采用银纳米粒子表面增强拉曼检测瓶装水中的DEHP[11]。 Zuo等用离子喷溅方式制备了银纳米基底, 并获得了乙醇中邻苯二甲酸二甲酯(DMP)的拉曼光谱[12]。 但是采用激光拉曼光谱技术快速定性及定量分析玩具塑料中的PAEs, 还未有报道。
本文采用激光拉曼光谱仪, 并结合理论计算, 研究了塑料玩具中PAEs的快速检测方法。 此方法无需样品前处理, 操作简单, 能够快速、 无损检测塑料中PAEs的种类及含量。 本文也根据海关提供的玩具样品, 验证了激光拉曼技术快速定性及定量分析PAEs, 准确度较高。 可满足玩具在进出口过程中海关的快速准确检测要求, 实现通关效率的提高。
根据RAPEX玩具及儿童用品召回通报及北京海关技术中心反馈, 塑料玩具中PAEs含量大于5%的超标情况占不合格率的99%以上, 因此本文校准曲线PAEs的浓度范围为5%~40%。 配制塑化剂重量百分比分别为5%, 10%, 20%, 30%和40%的参考物质, 称量PVC及BBP, DBP和DEHP, 分别加入到四氢呋喃中, 常温搅拌至完全溶解, 倒入表面皿中蒸发, 得到含有不同浓度的塑料塑化剂参考物质。
北京海关技术中心作为国家玩具检测重点实验室及CCC指定检测实验室, 承担北京市进出境玩具和儿童用品的法定检验任务和玩具产品的强制性认证检测工作。 儿童玩具检测样品由北京市海关技术中心提供, 为清关查验所得。 剪取玩具上一部分塑料用于拉曼光谱测试。 其中红色、 黄色、 绿色、 粉色样品为剪裁过的卡通玩具某一部分, 黄绿色样品为一段塑料绳。
实验采用自主研发的激光拉曼光谱仪(Smart 200, 钢研纳克检测技术股份有限公司), 扫描范围: 200~3 000 cm-1, 激光光源激发波长: 785 nm, 输出功率: 400 mW, 积分时间: 5 s, 累计次数: 20, 采用实验室自主开发的软件对拉曼光谱进行背景扣除处理。 气相色谱-质谱联用仪(GC-MS, 岛津GCMS-QP2010 Plus)测量玩具样品中PAEs的种类和含量。
为了使DEHP, DBP和BBP三种分子的理论拉曼振动结果更接近真实值, 选用6-31G劈裂价键基组对DEHP, DBP和BBP分子进行结构优化及模拟拉曼振动。 首先, 使用Gaussian软件, 应用B3LYP杂化泛函劈裂基组6-31G对三者分子结构进行优化。 在优化过程中, Optimization呈持续下降趋势, RMS Force, Maximum Displacement, RMS Displacement和Maximum Force均收敛, 且优化后的分子振动无虚频, 证明优化后的分子结构稳定, 能量最低。 优化后的PAEs分子两个酯基上的C—O, C=O键长相同, 酯基与苯环构成的两个C—C键长相同, 苯环各C—C键长基本相同, O—C—O键角接近120° , 数据均在实验误差范围内且符合分子结构理论。
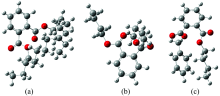
DEHP, DBP和BBP优化后的分子构型如图1所示, 基于此种结构可以看出三者均含有苯基、 酯基、 甲基, 三种PAEs的两个酯基一端与苯环相邻碳原子相连。 如图1(a)所示, DEHP酯基另一端与(2-乙基)己基相连, 构成1, 2双取代对称结构。 图1(b)显示DBP酯基另一端氧原子与丁基相连, 构成1, 2双取代对称结构。 而BBP两个酯基氧原子一个与丁基相连, 另一氧原子与单取代甲苯相连, 构成1, 2双取代不对称结构, 如图1(c)所示。 DEHP, DBP和BBP三者的结构特征决定了其拉曼光谱特征峰出现的位置, 也是本文用来判断玩具塑料中塑化剂种类的依据。
图2为PVC, BBP, DEHP和DBP的实验拉曼光谱图。 PVC中637和692 cm-1特征峰展宽较大, 导致玩具塑料拉曼光谱619和650 cm-1特征峰被覆盖, 但840, 1 000, 1 040, 1 580, 1 600和1 726 cm-1特征峰仍然存在, 可依据以上六个特征峰识别PVC中的3种PAEs塑化剂。 首先通过1 040 cm-1, 1, 2双取代苯环C—H变形振动、 1 580和1 600 cm-1, 1, 2双取代苯环C—C伸缩振动、 1 726 cm-1, 酯基C=O伸缩振动判定被测样品中含有邻苯类塑化剂, 然后通过特征峰的差异可进一步对邻苯类塑化剂进行定性分析。 其中图2b为BBP拉曼光谱图, 特征峰1 000 cm-1认为是单取代苯环C=C对称伸缩振动, 由图1(c)可知此特征峰仅BBP含有, 因此可用于定性BBP。 图2c为DBP拉曼光谱, 840 cm-1特征峰为丁烯基C—H面外摇摆振动, 未在DEHP拉曼光谱中观察到, 故认为840 cm-1可作为DBP定性依据。 同时对三种PAEs的1 040和1 726 cm-1特征峰强度比值, 得到DEHP系数为3.1±0.2、 DBP系数为1.8±0.2、 BBP系数为3.0±0.2, 认为通过该系数可定性DEHP。
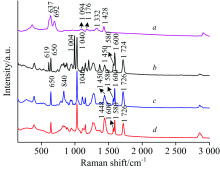 | 图2 PVC及PAEs拉曼光谱图 a: PVC; b: BBP; c: DEHP; d: DBPFig.2 Raman spectra of the PVC and PAEs a: PVC; b: BBP; c: DEHP; d: DBP |
基于密度泛函理论(density functional theory, DFT)方法基组6-31G计算DEHP, DBP和BBP理论拉曼光谱, 与实验拉曼光谱进行对比, 主要特征峰及振动模式归属如表1所示。 最大误差在DEHP 1 542 cm-1处, 为38 cm-1, 最小误差在BBP 621 cm-1处, 为1 cm-1。 表明计算结果与实际光谱数据基本相符, 说明了PAEs分子拉曼光谱特征峰归属正确, 进一步说明拉曼光谱能够用于玩具塑料样品中DEHP, DBP和BBP的准确指认。
| 表1 DEHP, DBP和BBP拉曼光谱主要特征峰及振动模式归属 Table 1 The main characteristic bands and assignment of vibration modes of DEHP, DBP and BBP |
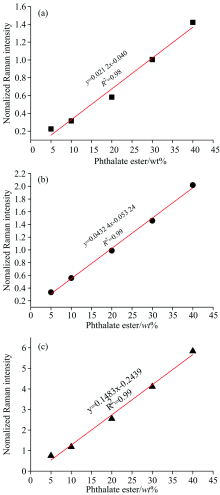
为了建立PAEs拉曼信号与其在样品中含量间存在的线性关系, 分别测试重量百分比5%, 10%, 20%, 30%和40%的参考物质, 每个参考物质随机选取三个位置, 每个位置重复测试三次, 结果如图3所示。 其中, 1 726 cm-1为PAEs酯基C=O伸缩振动特征峰, 是完整的高斯分布特征峰, 受背景及其他峰位干扰较小。 840 cm-1为丁烯基C—H面外摇摆振动, 是DBP的特征峰。 1 000 cm-1认为是BBP单取代苯环C=C对称伸缩振动。 694 cm-1为PVC特征峰, 峰强较强且干扰较小, 以694 cm-1与1 726, 840和1 000 cm-1峰强度的比值为纵坐标, PAEs含量为横坐标绘制线性拟合。 相比归一化, 将某一特征峰强度视为1, 其他特征峰强度为该谱峰强度的倍数, 在一定程度上认为是对信号强度的缩小。 本方法优势在于最小程度引入人为误差, 消除背景干扰及部分系统误差。 如图3所示, PVC中塑化剂的含量与与其特征峰强度呈一次线性相关。 相关系数r分别为0.98, 0.99和0.99, 准确度较高, 表明此方法能够用来进行PAEs的定量分析。
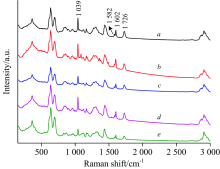
玩具塑料样品在拉曼测试前未对样品做任何前处理, 并采用实时背景采集模式进行测试。 图4显示了玩具塑料中不同颜色区域的拉曼光谱图, 从图谱中可以发现639, 695, 961, 1 040, 1 169, 1 437, 1 582, 1 602和1 726 cm-1等一系列拉曼特征峰。 由定性方法, 可知五个颜色区域的样品均是PVC中添加的DEHP。 经PAEs标准曲线定量分析, 可以得出玩具样品a, b, c, d和e中PAEs的含量分别为30.07%, 29.79%, 27.10%, 29.04%和14.56%。
采用GC-MS检测玩具塑料中PAEs的含量, 结果分别为31.39%, 31.86%, 24.65%, 32.530%和15.65%, 种类为DEHP。 与本文采用的PAEs定量校准曲线测定结果对比偏差为4.22%, 6.51%, 9.95%, 10.72%和6.99%, 满足定量分析的水平。 以上结果可以看出在室温自然光条件下, 样品暴露于空气中直接测试得到的校准曲线结果较好, 可达到精确定量要求。
为建立拉曼光谱检测玩具塑料中PAEs的快速筛查技术, 以DEHP, DBP和BBP为研究对象。 首先, 优化了三者的分子构型, 并采用DFT计算了三类塑化剂分子的振动光谱, 对比实验测得的DEHP, DBP和BBP的分子拉曼光谱进行指认并对分子振动模式进行归属。 其结果与实际光谱数据相符, 表明该方法对PAEs分子拉曼光谱特征峰的归属正确, 能够用于玩具塑料样品中DEHP, DBP和BBP的定性分析。 其次, 研究了拉曼光谱仪快速直接定量检测塑料中PAEs含量的方法。 结果显示DEHP, DBP和BBP的含量与其特征峰强度线性相关, 相关系数分别为0.98, 0.99和0.99, 表明此方法可以用于PAEs快速定量分析。 最后, 采用激光拉曼光谱仪, 在无任何前处理的条件下测试玩具样品。 优化采集过程中的背景扣除方法, 获得儿童玩具的拉曼光谱, 确认了PAEs的种类为DEHP, 并计算出其含量。 同时, 采用GC-MS进一步检测玩具塑料中PAEs的种类及含量, 和拉曼光谱得到的结果吻合, 从而验证了拉曼光谱技术快速定性及定量检测PAEs的准确性。 表明本文建立的激光拉曼光谱快速筛查塑料玩具中PAEs种类及含量的方法, 在不损坏玩具的条件下, 能够显著缩短检测时间。 在未来有望应用于海关现场货品的快速检测, 提高通关速度, 缓解海关压力。
| [1] |
|
| [2] |
|
| [3] |
|
| [4] |
|
| [5] |
|
| [6] |
|
| [7] |
|
| [8] |
|
| [9] |
|
| [10] |
|
| [11] |
|
| [12] |
|